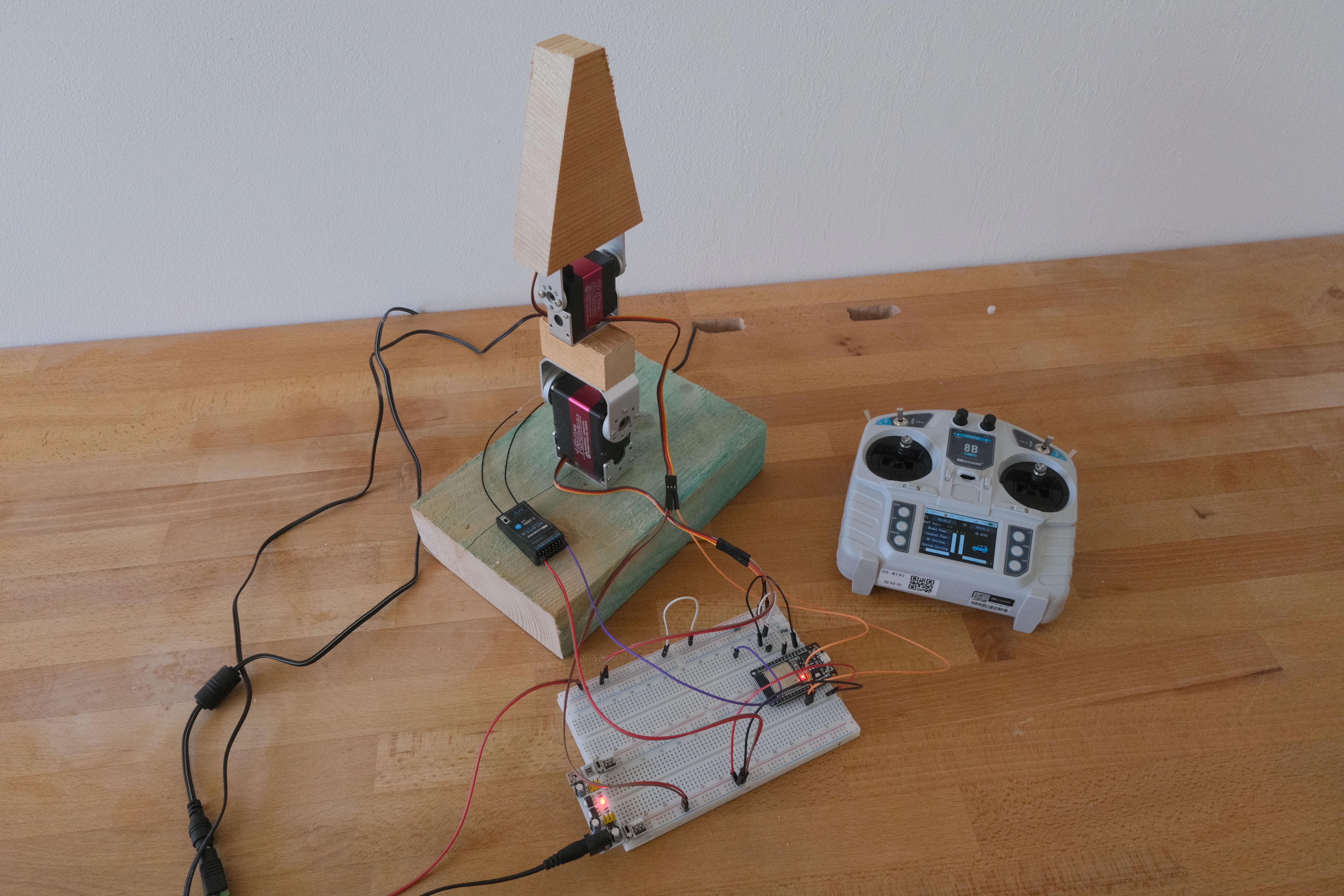
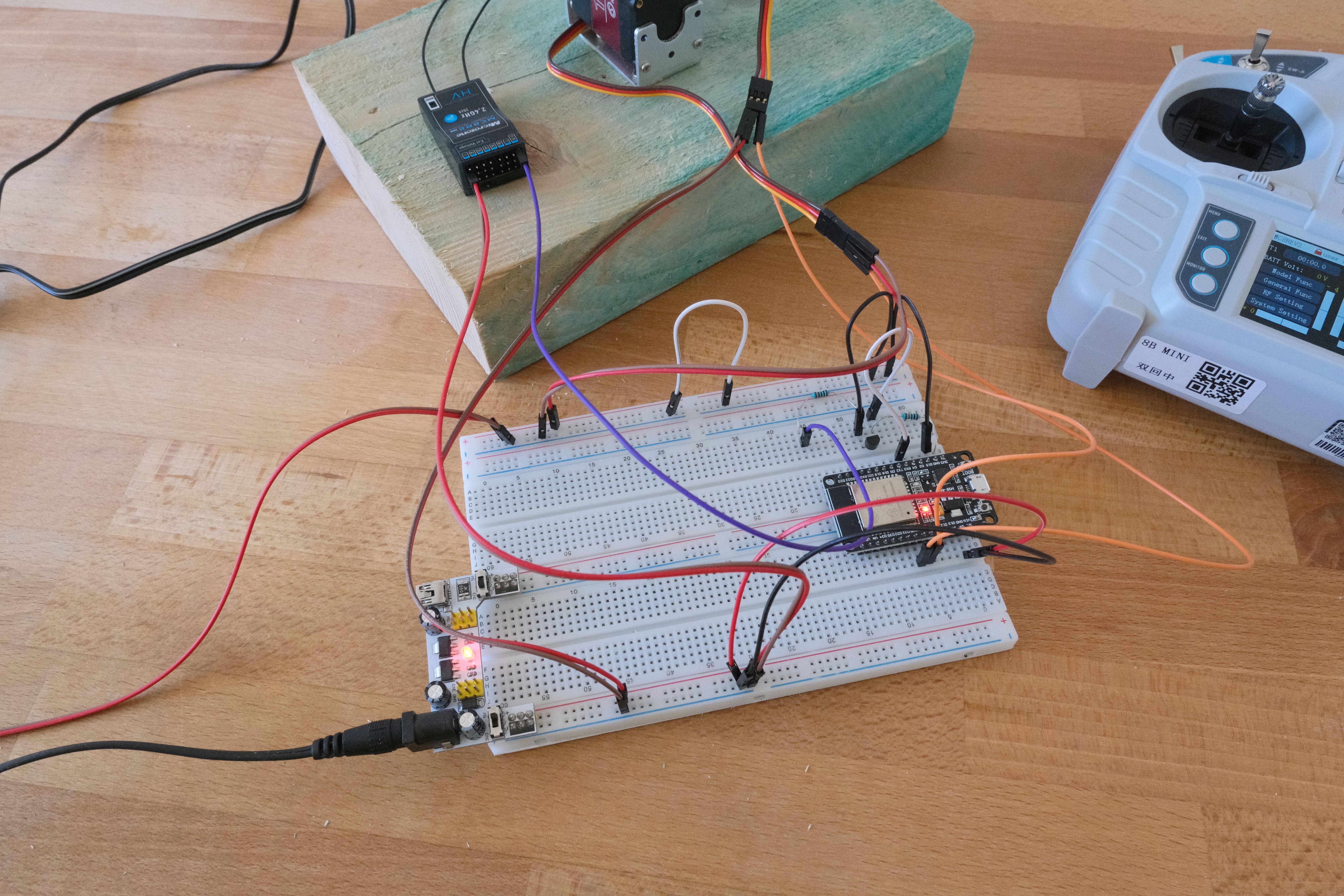
With libraries for Servo (ESP32Servo) control and SBUS communication, the low level stuff becomes easy.
Received values need to be transformed to corresponding servo control values. Additionally, input smoothing helps to prevent jitter.
In this guide, all the things are integrated together to achieve the above.
Disclaimer: This how to is intended for advanced users. You should be able to understand what commands are doing, before copy-pasting and executing them.
Prerequisites
Main parts:
Arduino Due,- Arduino Due board is not supported by SBUS library,
- ESP32 was used as an alternative.
- MC8B-mini and MC8RE-V2 - remote and corresponding receiver,
- 2 PWM servos.
- power supplies corresponding for your servo and board.
Electrical components:
- 10 kΩ resistor and 1kΩ resistor,
- NPM transistor, i.e. BC237/238/239.
- other wiring ingredients of yours choice.
Health, life and property safety warning
With high power devices and strong torque, this is very important.
Things could go wrong, and connection between remote control and the control board could be interrupted due to various reasons. Then, the device should gracefully handle the issue and shutdown/stop/behave according to what’s the safest behaviour for it.
There also should be other (physical) controls allowing user to execute emergency stop.
Also, based on application, things should be user-fault tolerant. And, there should be checks. At least, not allowing servo to rotate more, than what’s possible by physical construction of the device.
This guide shows the happy scenario, only.
Wiring
Powering MC8RE-V2:
- “positive electrode” to 5V power supply - either provided by board or external,
- “negative electrode” to GND - all connected together.
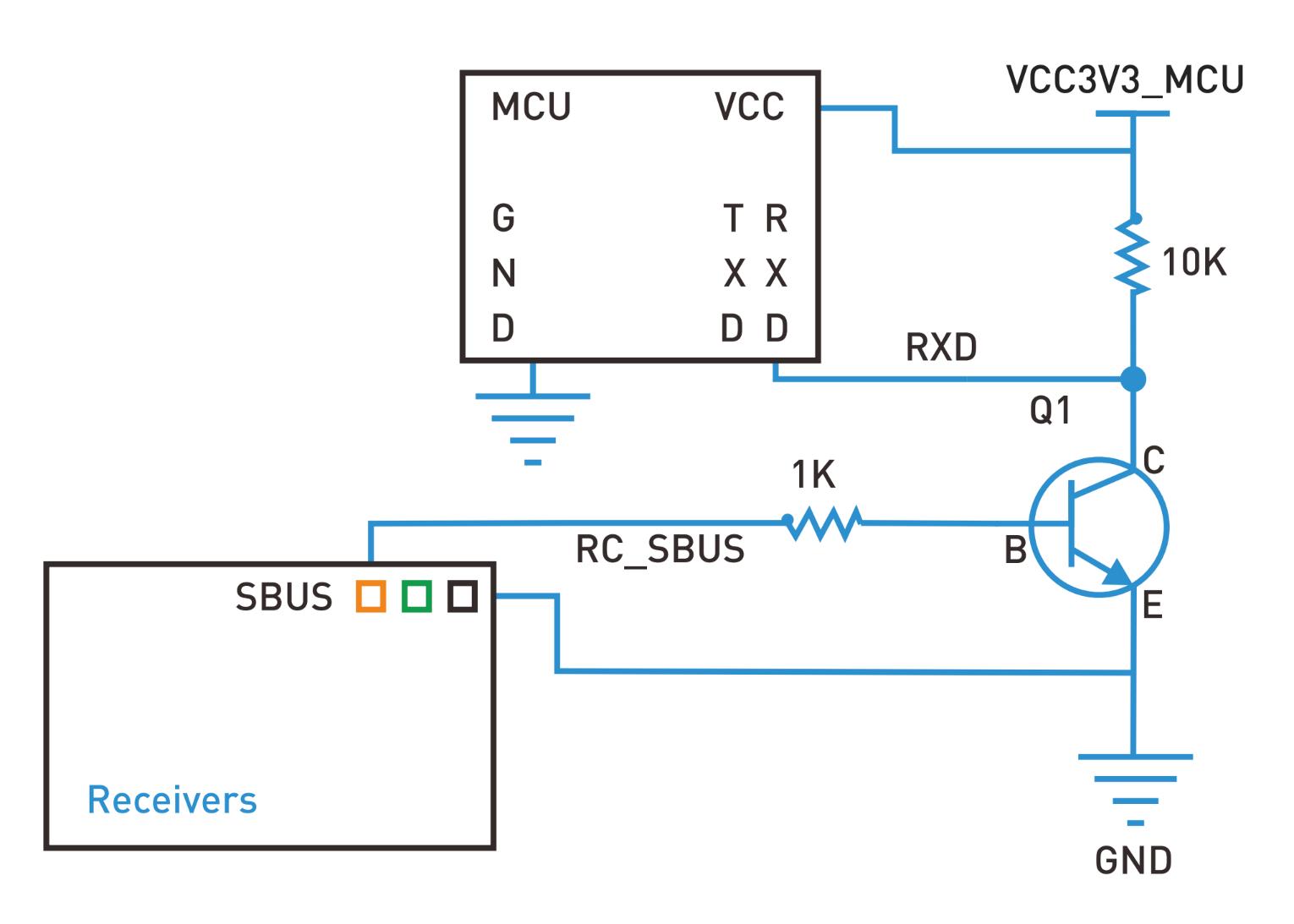
Providing SBUS signal from MC8RE-V2 to the board:
- put 10kΩ resistor between 3V3 and NPN transistor’s collector,
- put 1Ω resistor between SBUS output and NPN transistor’s base,
- NPN transistor’s emitter to GND - all connected together,
- input pin (e.g. RX for Serial 2) to NPN transistor’s collector.
Connecting servo:
- + to power corresponding supply,
- - to GND - all connected together,
- S to board’s output pin (e.g. 25 and 26).
Arduino Due - not supported by SBUS library
Unfortunately, Arduino Due is the only Arduino board I’ve got currently available, and the SBUS library doesn’t support this board:
/.../Arduino/libraries/SBUS/src/SBUS.cpp:74:4: error: #error unsupported device
#error unsupported device
^
exit status 1
Error compiling for board Arduino Due (Programming Port).
Maybe in the future I’ll create the code for Arduino board once I have Arduino board supported by SBUS library, or SBUS library gets support for Arduino Due.
Alternative - ESP32 programmed with Arduino
Arduino’s standard library doesn’t support servo control for ESP32.
Lots of libraries didn’t build, but luckily I found one from multiple libraries I tried, and this one worked https://github.com/madhephaestus/ESP32ServoServer.
#include "SBUS.h"
#include <ESP32Servo.h>
class SmoothingInputScalingServoControl {
static const int smoothing_samples_count = 32;
public:
SmoothingInputScalingServoControl(
int servo_pin,
int input_min,
int input_max,
int angle_min,
int angle_max,
int servo_min,
int servo_max,
bool reverse_direction
):
servo_pin(servo_pin),
input_min(input_min),
input_max(input_max),
angle_min(angle_min),
angle_max(angle_max),
servo_min(servo_min),
servo_max(servo_max),
reverse_direction(reverse_direction)
{
for (int i = 0; i < smoothing_samples_count; i++) {
inputs[i] = (input_max - input_min) / 2 + input_min;
}
}
void attach() {
servo.attach(servo_pin, servo_min, servo_max);
}
void update(int new_input) {
inputs[next_input_slot++] = new_input;
// condition-less index rotation - if it reaches smoothing_samples_count, then
// division yields 1, and its substration multiplied by smoothing_samples_count results in zero
next_input_slot = next_input_slot - (next_input_slot / smoothing_samples_count) * smoothing_samples_count;
// note: there's an optimization possible that doesn't require iteration
// sum can be maintained and stored,
// substract previous (overwritten value),
// add new updated value
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < smoothing_samples_count; i++) sum += inputs[i];
int average_input = sum / smoothing_samples_count;
// clamp the input based on limits
int average_input_clamped = max(input_min, min(input_max, average_input));
// integer based multiplication and division requires multiplication to happen first
int angle = reverse_direction == false ? (
angle_min + ((average_input_clamped - input_min) * (angle_max - angle_min)) / (input_max - input_min)
) : (
angle_max + -((average_input_clamped - input_min) * (angle_max - angle_min)) / (input_max - input_min)
);
// TODO for SAFETY - WARNING: the servo will try to move to the desired position
// with high power servos, this can result in DAMAGE or HEALTH INJURY,
// this is not handled by this code
servo.write(angle);
}
Servo servo;
int servo_pin;
int input_min;
int input_max;
int angle_min;
int angle_max;
int servo_min;
int servo_max;
bool reverse_direction;
int inputs[smoothing_samples_count];
int next_input_slot = 0;
};
SBUS mc8re_SBUS(Serial2);
uint16_t mc8re_channels[16];
bool mc8re_failSafe;
bool mc8re_lostFrame;
const int mc8re_channelsCount = 8;
SmoothingInputScalingServoControl axis_a_control(25, 250, 1750, 0, 180, 500, 2420, false);
SmoothingInputScalingServoControl axis_b_control(26, 250, 1700, 0, 180, 500, 2420, true);
const int axis_a_channel = 4 - 1;
const int axis_b_channel = 2 - 1;
void setup() {
mc8re_SBUS.begin();
axis_a_control.attach();
axis_b_control.attach();
}
void loop() {
if (mc8re_SBUS.read(&mc8re_channels[0], &mc8re_failSafe, &mc8re_lostFrame)) {
// TODO for SAFETY - WARNING: the handle mc8re_failSafe needs to be handled in real world applications,
// i.e. emergency shutdown, emergency stop, or else emergency handling or after some delay
// the most likely not so critical with servo, but uncontrolled high power motors can result in DAMAGE OR HEALTH INJURY
axis_a_control.update(int(mc8re_channels[axis_a_channel]));
axis_b_control.update(int(mc8re_channels[axis_b_channel]));
} else {
// TODO for SAFETY - WARNING: failure to read input needs to be handled real world applications,
// i.e. emergency shutdown, emergency stop, or else emergency handling or after some delay
// the most likely not so critical with servo, but uncontrolled high power motors can result in DAMAGE OR HEALTH INJURY
}
delay(1);
}
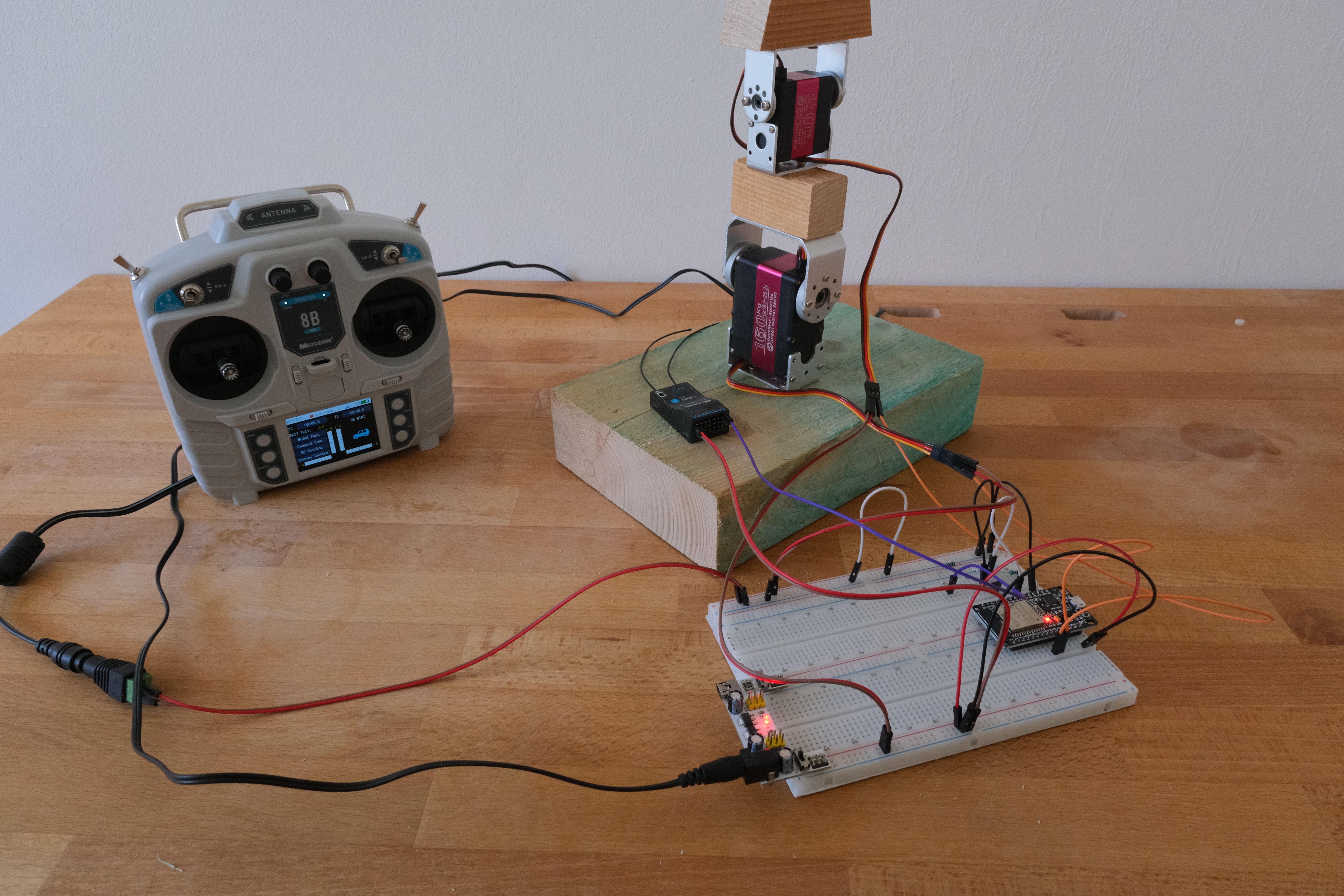
Demonstration of functionality with ESP32: